Metal Melting Furnace
- This metal smelting equipment is designed based on the innovative (IGBT) induction technology developed from years of research. These are highly efficient products that have helped to achieve amazing results for various foundries and laboratories.
- The furnace can work with a power rating ranging between 3.5-160kw which is a fairly wide range and reduces the amount of power required, thereby cutting electricity costs.
- The metal melting kiln has an advantage over other types of furnaces:
- The gas furnace for example often has few controls as opposed to the (IGBT) induction technology in which the amount of heat being supplied can be varied based on the power supplied.
- The resistance furnace is quite effective, but it still underperforms compared to the induction furnace in which there is no combustion and therefore only the heat required to melt the metal is supplied.
- Induction melting furnace kit has been designed with the convenience of the operator in mind. The crucible is detachable and can easily be replaced; this makes it easy to clean the crucible and also ensure a seamless transfer of operations between various metals to be melted.
- A digital display helps to easily read the temperature within the furnace. An omni-directional warning system has also been included to ensure the safety of both the operator and the plant.
- Speedy melting rate within 2 min per batch
- Portable design, small size, light weight
- Speedy melting rate within 4 min per batch
- Built in water pump, easy to cool
- The full melting time is less than 5 mins
- Suitable for 10kg gold or 4kg platinum melting
- Used to fuse large amounts of metals
- Used for casting large and heavy parts
- Designed for 10-50kg non-ferrous metal melting
- Motor drive chain to complete pouring
- Designed for 50-250kg non-ferrous metal melting
- Hydraulic tilting to improve stability operator’s safety
Why Choose SuperbMelt Metal Melting Machines
How to Melt Metal: Metal Melting Furnace Buying Guide
For centuries, metals have been put to great uses, from iron to copper, zinc, aluminum, silver and gold. There are metal appliances or devices used at homes, offices, companies, and manufacturing plants. Without metals, we probably won’t have the opportunity to have cars, electricity, buildings, roads, and other necessary infrastructures today.
However, it is imperative to obtain metals in their purest and greatest forms before we can use them. To achieve this, it becomes very important that metals be melted and processed accordingly.
This guide explains the essential procedures that must be followed while melting metals. More importantly, it details the types of equipment or melting furnaces we need to have before doing any of these melting procedures. You will also read about how to perfectly operate these metal melting machines.
This metal melting guide is produced to simplify the entire metal melting process so that when you are equipped with the right metal melting furnaces, you can carry out the procedures with outstanding success. Efforts are made to provide some examples of furnaces that are affordable and can be found everywhere, most especially those produced by the Top Ten Manufacturers of multi-metal melting furnaces listed in this guide.
Get your metal melting furnace kit ready and get to work!
Let’s dive right in:
Why Metals Need Smelting: Metal melting machine in the foundry industry
Metals exist in two distinct forms: In their alloyed or non-alloyed states. As an alloyed material, it means that metals are mixed with other metals or non-metal substances or compounds. And, in this case, it is considered impure because it contains other materials that may be undesirable.
Even though they may be obtained in their non-alloyed form, it is still important to extract the purest form of these metals before they can be put to commercial uses.
Metals have remained an essential part of human life, and they have been used in building your cars, homes, electrical and mechanical appliances, roads, and several other vital projects that sustain humanity.
This is why it is imperative that metals are smelted or melted in order to obtain the pure metals you need for all different purposes in your daily life.
1.1, Metal melting to purify
The main reason why metals are melted or smelted is that you need to obtain them in their purest states for your usages.
Take for instance, iron comes in different alloys such as Anthracite iron (with carbon), Fernico (with nickel and cobalt), or Cast iron (with carbon).
Since what you need to make your electrical and mechanical appliances, for instance, is pure iron. Hence, it becomes very important that you should first purify iron before you can use it.
This requires that you should melt iron alloys for the purpose of separating other materials such as carbon, nickel or cobalt from iron.
1.2, Metal melting for casting
When melted, a metal goes through some significant changes as described below:
Alloy/impure metal –> Molten state –> Cool/cast form
When heat is applied to an alloy of metals, they melt at their respective melting points, turning into their hot, liquified form known as molten metals.
For instance, cast iron melting point is 1,204 ℃ and aluminum melts at 659℃. When cooled down, the liquified and hot metal turns into a solid state again. The difference in this process is that the final metal is now purified and ready to be used for commercial or industrial purposes.
Metal melting can be done by applying different methods: From a small-scale home-based melting using a small flame source to the one conducted in a small foundry. However, because of their constant usage in large amount, metals can now be smelted using sophisticated machines and equipment such as metal melting furnaces.
This guide is specifically written to explain how metals are melted nowadays using these furnaces. The procedures used to operate the furnaces are also simply explained.
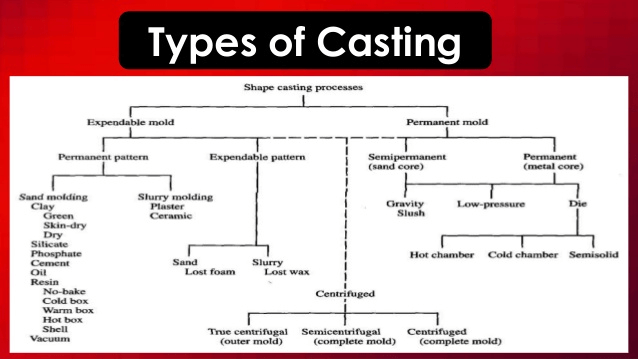
Figure 1: Types of casting, obtained from Slideshare
There are two main types of metal casting—expendable mold metal casting and non-expendable mold metal casting (permanent mold). Figure 1 above reveals the processes required to achieve these two stages of casting, and it also reveals their respective final outcomes.
1.3, Metal melting for industrial uses
Metals and their alloys such as iron, brass, steel, copper, aluminum, and others have significant industrial usages.
For examples, steel is used in shipbuilding, scaffolding for homes, and for other structures that need fortification. Iron is used in making electrical and mechanical devices. Copper can be found in electrical wires, cables, and as internal components of electrical and mechanical appliances.
Most heavy-and low-duty machines and equipment used in factories and other manufacturing units are made from metals.
This is why it is very important to extract metals from their alloys so that they can work well. In their alloys, metals will not be able to perform as expected.
For instance, phosphor bronze is a copper alloy, and it does not conduct electricity as the real copper itself. And to obtain pure copper, its alloy must consequently undergo melting and casting.
How to melt metals nowadays
There are different methods used to melt metals nowadays. This depends entirely on the scale of the melting operations and the environments they will be taking place. It is possible for people to melt metals at home, in a small or big foundry, or in a large-scale industrial setting. Each of these operations requires special equipment or machine, as described below.
2.1, Melting metals using low-burning flames at home
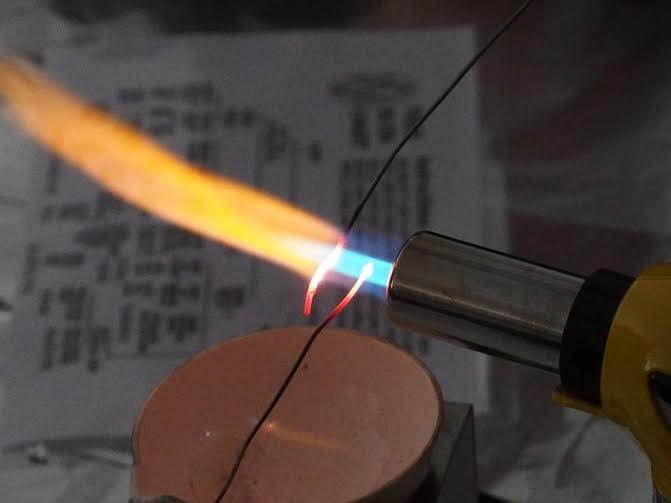
At home, it is possible to melt some metals using a simple tool such as a low-burning flame. And gas burners are examples of a low-burning flame.
Picture of low-burning flame obtained from Public Lab
Table 1 below indicates the amount of heat produced by some fuel gases when they are burnt with either oxygen or air:
| Fuel Gas | Combustion with Oxygen (oC) | Combustion with Air (oC) |
| Acetylene | 3480 | 2500 |
| Butane | 1970 | |
| Carbon Monoxide | 2121 | |
| Ethane | 1955 | |
| Hydrogen | 3200 | 2210 |
| MAPP1) | 2927 | 2010 |
| Methane | 1950 | |
| Natural Gas | 1960 | |
| Propane | 2526 | 1967 |
| Propane Butane Mix | 1970 |
Table 1: Flame temperatures for some commonly used fuel gases, obtained from Engineering Toolbox
The Process: Using a low-burning flame to melt metals is as simple as it seems. All you need to do is to first select your burner’s fuel gas and decide whether you are going to use oxygen or air. As revealed in Table 1, using oxygen produces a flame with better heat than air.
Table 2 below shows some metals and their corresponding melting points in (°F/°C):
| Metal | Fahrenheit (oF) | Celsius (oC) |
| Aluminium | 1218 | 659 |
| Brass | 1700 | 927 |
| Bronze | 1675 | 913 |
| Cast Iron | 2200 | 1204 |
To melt a piece of Brass, which has a melting point of 927℃, an oxyacetylene flame can be used. An oxyacetylene flame produces maximum heat at 2,500℃.
NOTE: An oxyacetylene flame is produced from the combination of acetylene gas and oxygen.
2.2, Melting metals in a foundry
Foundries are factories built for the purpose of melting and casting metals. Depending on the size of the melting operation, it could be a small, medium, or a large one.
However, the procedures carried out at different foundries are somehow similar, and they are outlined below:
- Melting: High heat is applied to the metals to be melted. Different metals will melt when they reach their melting points. In modern foundries, heating machines or furnaces are used to melt metals.
- Degassing: This process involves removing excess hydrogen present in the molten metal. This can be done through a chemical reaction in the cast material or by physically entrapping the gas during the casting procedure.
- Making molds: It is important that the appropriate molds are designed and produced for the molten metal before casting. The particular mold chosen depends on the types of casting.
- Pouring of molten metal: Once the molds have been made based on the desirable patterns, the next process is to pour the molten metal into the molds during the casting process.
- Shakeout: This refers to the process of separating the solidified metal component from its molds.
- Degating: This procedure involves removing runners, heads, risers, and gates from the casting.
- Heat treatment: When you want to change the shape, metallurgical, chemical and/or physical properties of a metal, you will be required to carry out heat treatment on the metal.
- Surface cleaning: To remove sand and other molding materials that are attached to the metal after degating and heat treatment, you will need to do some surface cleaning on the metal.
- Finishing: The final processes that must be carried out on a metal include grinding, machining, and sanding. These are required in order to give the metal components desirable shape, dimensions, and brightness (surface finish).
2.3, Melting metals in a foundry
Lately, the process of melting metals involves the use of sophisticated equipment or machines such as furnaces.
Tilting Type Platinum Melting Furnace obtained from SuperbMelt
Unlike open foundries, metal melting furnaces are more advanced and equipped with features that streamline the entire melting process. Most furnaces offer speedy melting rates, and they can be automated to work round the clock. They have the capacity to manage heat energy, unlike foundries that allow heat to escape to the environment.
As a result of this, metal melting furnaces save energy and they are mostly environmentally friendly.
With furnaces, there is almost no loss of metals. And casting can be done under pressure without any shrinkage. During melting, metals are protected against oxidation. Some furnaces even possess autodiagnosis system.
Metal melting furnaces are mainly used at the industrial level because they are capable of handling large amounts of metals at a time.
Furnaces used for melting metals are capable of melting to a high degree temperature ranging from 1000℃ to as much as 2000℃ and over.
Copper Melting Furnaces
At the industrial level, copper is now melted using some specific copper-melting furnaces. Apart from the fact that the use of furnaces is considered environmentally friendly, it is also energy-saving (because energy is not lost to the surrounding as it usually occurs in the foundries), and the materials are protected from oxidation, wastage, and other major melting problems.
3.1, Origin of Gold Digger (Origin of Gold Digging)
Highlighted below are some different types of copper melting furnaces:
3.1.1 Induction melting furnace
The induction furnaces for melting copper come in two main kinds as described below:
Double push-up furnaces: When you are considering melting copper on a small-scale or for prototyping, double push-up furnaces are the best choice for those kinds of operations. This type of furnace utilizes a single-shot principle whereby a small amount of the metal can be melted in only one shot.
The video below reveals how just a shot of copper material can be melted using this equipment.
The main advantage of this approach is that the copper can be quickly melted. And the procedure can be repeated for as many times as possible until the required amount of molten copper has been obtained. The process can be started or stopped anytime, thereby making this method to be very flexible and manageable.
The melting time is very short for this copper melting type; so, it is not necessary to use cover gas to prevent the molten copper from absorbing oxygen.
However, if it is needed, a cover of inert gases may be used. Double push-up furnace is useful for maintaining the life cycle of rod die-casting. And since the crucibles are small in size, a rod of chopped copper can be used instead of sheared cathode as the melt shock.
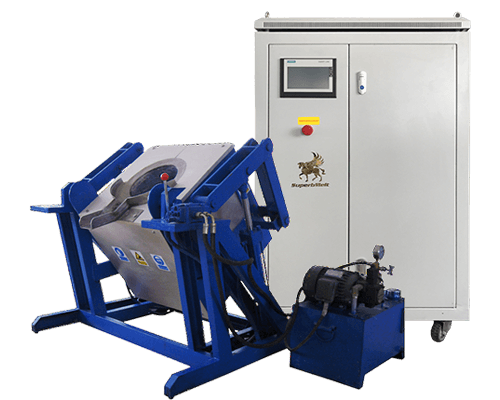
Tilting furnaces: It is advisable that the tilting furnaces should be used when considering melting a large amount of copper in a continuous melting operation.
Large crucibles are used in this occasion, and they make it possible to adopt better flexibility in choosing charge material, chopped wire, sheared cathode, electrical grade copper that is of high quality, or shop around for scrap such as runners and biscuits.
A ceramic or metal cover is used (above the crucibles) to prevent the molten copper from absorbing oxygen. Similarly, a gas cover that consists of nitrogen and 5% hydrogen is used to cover the liquid metal’s top.
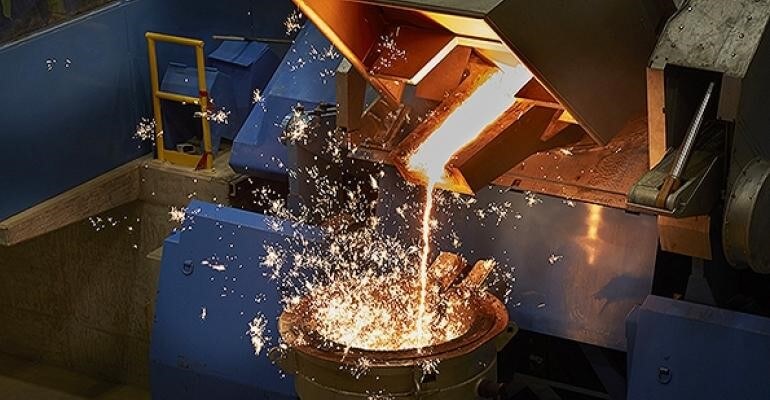
The furnace is tilted hydraulically or otherwise once the copper has reached the right temperature. By doing this, a desirable amount of liquid copper can be poured into a ceramic cup. The liquid copper in the cup will then be taken to the die-casting arm of the machine by a controlled robot.
There are different types of tilting copper melting furnaces: We have hydraulic, chain, and manual. Some furnaces have a power of 25kW and adjustable power of 25kW. Their voltage is in three phases, up to 380V or above.
The capacity of some copper melting furnaces ranges from 15kg to as large as 30kg. Their maximum temperature is 1800oC, with an average melting time of 5-8 minutes.
They are capable of working nonstop for 24 hours to increase overall productivity. Some of them have omni bearing alarm system which helps to maintain ultimate safety during operations.
As its name implies, gas fired furnace derives its power from gas. This can be natural gas or propane that has gas and air in adjusted proportions. A gas furnace will provide you the required heating.
Whether you are using it in your home, foundry or workshop, it works as long there is enough gas supply for the furnace to function. Common gases can produce heating between 300-400℃. However, butane and propane can produce heating temperature close to 1,970℃.
A gas fired furnace, produced by Carrier
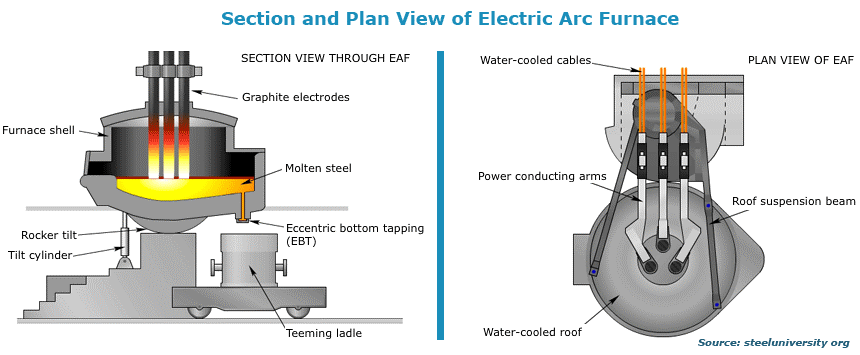
3.1.3 Arc furnace
Arc furnace is useful for producing carbon steels and alloy steels. An arc furnace uses electrical energy to produce the necessary heat. This is why it is called Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). It works by recycling iron scrap in an EAF scrap/manufactured iron units like pig iron, iron carbide, and DRI. Scrap is the most common feedstock for EAFs, which accounts for 80 percent of materials used in arc furnaces.
For the melting process, units of iron are mixed with limestone to form slag that will be fed into the arc furnace. EAF converts the raw materials into liquid steel as quickly as possible. The steel produced is further refined by other steelmaking procedures. In fact, any kind of operations is possible in the bath operation period—when the steel is still in a liquefied form.
To obtain the needed heat or temperature, an EAF needs about 350-370 kWh per t-steel.
3.1.4 Resistance crucible melting furnace
A resistance crucible melting furnace is used for melting metals. The material to be melted is held in the crucible where the temperature is controlled. In the case of a resistance crucible melting furnace, the crucible itself is a separate unit; once loaded with the metal to be melted, it is placed in the furnace. Through this approach, it is possible for the temperature in the crucible to be controlled.
There are different types of crucibles: Graphite, silicon carbide, and cast iron or cast steel crucibles. The crucible can either be fixed or tilting. A tilting crucible can be titled to pour out the molten metal from it. On the other hand, a fixed crucible is immovable.
Crucible furnace can be easily operated, with low investment and maintenance cost. However, it is not suitable for melting large amount of metals. The melting time of crucibles are important to determine the energy consumption cost.
It is estimated that the melting time for 350 kg crucible is 85 minutes, while it is 130 minutes for 800kg crucible. Some crucibles have capacities up to 1500kg. And the average amount of electrical energy required for melting 1 ton of aluminum to a temperature of 720℃ is around 400kWh.
3.2, How SuperbMelt copper melting furnace works
The processes required for melting copper in an induction furnace are outlined below, irrespective of the type of copper melting furnace utilized:
- Start water chiller for cooling
- Turn on the main power switch
- Put the material to be melted (copper) in the crucible
- Press start button
- If necessary, adjust the power
- The copper will be melted in the crucible
- You can use speedy melting process for like 8 minutes
- Once the melting has been completed, press stop button
- Do manual tilting to control the pouring of the liquid (molten) copper (remember that this tilting can also be done using a hydraulic system or chain)
- Turn off the main power switch after 5 minutes
3.3, Conditions necessary for good copper melting
When using furnaces to melt copper, it is essential that strict attention should be paid to the following precautions:
- Furnace conditions: It is imperative to check whether the copper melting furnace is in good conditions. Look at the switch and buttons and see that they are perfectly connected to the inductive source of power (induction system). Check the inside of the crucibles and confirm that they do not contain any impurities. Make sure that the hydraulic, chain, or the manual pulling system is working before starting any copper melting operations.
- Cover gas: It is mostly advisable to use inert gases as the cover gas when melting copper. The primary reason for this is that it performs better in the process of preventing liquid (molten) copper from trapping some oxygen. The major issue with oxidation of molten copper is that it could affect its physical properties such as its color, ductility, tensile strength, and so on.
- Cover materials: The best practices adopt the use of a metal or ceramic cover for copper melting operations. These cover materials also prevent oxygen from having contact with the molten copper.
- Copper quality: The overall time it takes for the copper to melt depends on its quality. If it contains much impurity, it may take a longer time for it to melt. Some alloys of copper melt at different temperatures and timing.
- Spacious place for equipment installation: It is not proper to install the furnaces in a small space because this may restrict the free movement of the workers melting the material (copper). This is also in compatibility with paying attention to the environmental effects of copper melting. A spacious place is expected to be more aerated and better for maintaining the temperature within the workshop or place where the furnaces are installed.
Iron & steel melting machine
Steel is an alloy of iron, carbon and other materials. This accounts for the reason why steel melting points are slightly higher than that of iron, as shown in the table below:
| Type of Steel | Melting (oC) | Type of Iron | Melting point (oC) |
| Carbon Steel | 1425-1540 | Iron, Wrought | 1482-1593 |
| Stainless Steel | 1510 | Iron, Gray Cast | 1127-1204 |
| Maraging Steel | 1413 | Iron, Ductile | 1149 |
| Alloy Steel | 1415- 1432 | ? | ? |
| Tool Steel | 1400- 1425 | ? | ? |
Both iron and steel have industrial usages or applications. For examples, steel is used as a component in automobiles, weapons, electrical appliances, buildings, tools, infrastructure, and ship. Iron is also used in buildings, ships, boats, rails, and as iron cylinders in steam engines.
To retain their great physical, metallurgical, and chemical properties, it is important to put some alloys of steel and iron through the process of melting.
4.1, Different kinds of Iron & Steel melting machines
You may need to check out some electric melting furnace for sale catalogues or websites to discover which one will be the most appropriate for you. Highlighted below are different types of iron and steel melting machines:
4.1.1 KGPS aluminum shell induction melting furnace
The principle of KGPS aluminum shell or frame induction melting furnace lies in the fact that the device can convert three-phase electric power into one and use it to create electrical energy that will be used for heating metals. The heat produced through this process can be used to complete the remaining procedures in melting and casting process, which include sintering, forging, and forming bent tubes.
Some KGPS aluminum shell induction melting furnaces come with an air chiller for SCR, electricity auto breaker, water relay to protect the power supply, water-temperature-protecting system, and pipe for the power supply. Some are flexible to operate and can manage a power supply between 200kW and 5000kW.
4.1.2 KGPS steel shell induction melting furnace
KGPS steel shell or frame induction melting furnace is useful for melting and holding ferrous and non-ferrous metals. It has a capacity of 1t/h to 30t/h. It is environmentally friendly, and this is why it is adopted in many foundries that face the problems of emitting plenty of dust and other pollutants. It can handle power between 250kW and 30,000kW.
Above all, it utilizes the KPGS technology, which involves converting three-phase power into one to obtain a concentrating heating system.
It has a frequency-scanning device such as zero-voltage soft start mode. It has a constant power control board that monitors the changes in voltage and current/power to guarantee effecting melting.
The power supply is maintained with a dependable circuit protection structure named SCR overvoltage and over-current protection. It also has water-temperature protecting system. And the furnace is easy to operate.
4.1.3 IGBT induction melting furnace
The most interesting aspects of the IGBT melting furnace are the unique features it consists of. Some of these great features are highlighted below:
- Lower power consumption
- Higher or increased melting efficiency
- Reduced amount of noise
- Small land requirement—it can be installed on a small piece of land
- Reduced air pollution
- Operating it does not require elaborate training
The IGBT induction melting furnaces are very popular in metalmaking companies because they are efficient and help companies save on energy and other costs.
4.1.3 Past steel and iron melting methods
The steel and iron melting procedures are somewhat interconnected as explained in this section. Steel is, technically, produced from iron. When we melt iron from its ores, it usually has more carbon than is needed or necessary. However, to convert that to steel, we must first reprocess the iron to obtain the right amount of carbon before adding other substances to that in order to produce our steel.
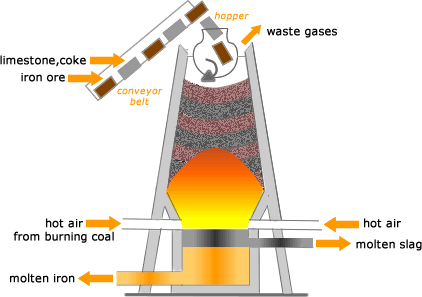
Modern iron and steel melting involves using some sophisticated furnaces, mostly induction furnaces. However, before this time, steel was mainly produced using an old method known as blast furnace. Iron was also melted in a blast furnace before.
As shown in the picture above, iron ore is fed into the blast furnace, together with limestone and coke. Hot air from the burning coal is allowed into the furnace to melt the iron. In the process, the molten slag and molten iron can be collected separately. The picture below reveals a typical blast furnace used in melting steel, which typically has higher melting points than that of iron.
A blast furnace (for steel) obtained from Business Journals
NOTE: Due to its pollution effect on the environment, blast furnace was somehow replaced by another method to produce iron some decades ago. This process was called Direct Iron Reduction, and it comprised of two major reactions:
Reaction 1: 2 CH4 + O2 –>2CO + 4H2 (Natural gas is oxidized, partially with heat and catalyst)
Reaction 2: Fe2O3 + CO + 2 H2 –> 2 Fe + CO2 + 2H2O (The gases produced in Reaction 1, carbon monoxide and hydrogen, are eventually treated with iron ore in a furnace, leading to the production of “sponge iron”, which is very good in manufacturing steel).
The two types of blast furnaces shown in this section have now been replaced by a better, environmentally friendlier, and more effective method of melting metals—which is through the use of an induction furnace.
Here are some of the benefits of using induction furnaces for steel and iron production:
- Mass production: With induction furnaces, it is possible for metallurgical companies to produce large amount of steel and iron within a short period of time. This is possible because induction furnaces allow large quantities of iron and steel to be melted, unlike the older methods.
- Cost-efficiency: Using an economy of scale, companies can reduce the cost of melting steel and iron. The induction furnace requires less energy, and it does not waste energy into the atmosphere like other previous methods.
- Controlled melting procedure: The temperatures of induction furnaces can be controlled. For steel, it is sometimes important to control the heat output of the furnace. This is done by varying the percentage of temperature/heat reaching the steel during melting.
4.2, Different kinds of Iron & Steel melting machines
The induction furnace for melting iron and steel follows similar procedures outlined in Section 3.2 for copper melting. However, the principle guiding steel melting is slightly different from that of iron or copper.
The major difference is in the capacity that steel furnaces can manage. Most induction furnaces used to melt steel can handle between 10 kg and 50 tons of steel. The small capacity melting furnaces can melt up to 500kg of steel, while the large, industrial furnaces can deal with up to 50 tons of steel.
4.3, Conditions necessary for good iron & steel melting
Melting iron and steel require some important conditions that must be taken care of. These include but are not restricted to:
- Proper temperature control: If you are using the same furnace to melt iron and steel, you must pay serious attention to the furnace temperature. This is because the melting points of steel and iron are different (as shown in the table in this section). If you fail to set the temperature appropriately and let either steel or iron reach their melting points, you may obtain an unsatisfactory outcome.
- The induction furnace structure: Only utilize the induction furnaces that are built for the purpose of melting iron and steel. These furnaces have heavy, structural parts that can withstand high temperatures and pressures. The crucibles must be very strong and capable of handling huge amount of steel or iron at a time. Too much heat can cause internal coil losses or sparking. So, it is advisable that you use the best induction furnaces that can stand these extreme heat condition.
- Adaptability: Your chosen iron and steel melting furnace must be adaptable to every kind of required situation. Sometimes, you may have to increase the temperature. Or it may be necessary to work round the clock, for 24 hours. At that time, the furnace will be so hot. If the furnace is made with materials that are not flexible or adaptable to the melting requirements, the machines could develop some mechanical or electrical faults.
Summary
Chapter 4 critically looks into the different types of old and modern melting methods for iron and steel. These include KGPS aluminum shell induction melting furnace, KGPS steel shell induction melting furnace, IGBT induction melting furnace, and so on. Efforts are made to explain how they work. Some conditions are required so that the induction melting furnaces can perform at their optimal level, and these conditions are simply described in this section. Iron and steel melting is very important because of the widespread commercial usages or applications of the two metals in our world. To purchase these furnaces, you may need to look around for “metal foundry for sale” advertisements online or elsewhere where there will be adequate information about metal melting furnace for sale.
In some circumstances, you can reduce the cost of starting your foundry by buying a used aluminum melting furnace for sale. This can be appropriate for a small metal furnace factory. Or you may purchase a used induction furnace for sale that will make it easy to melt metals. Even though it is quicker to order directly from manufacturers, some metalworking businesses go around looking for metal smelter for sale, electric foundry for sale, small furnaces for sale, or even smelting equipment for sale.
Whatever choice you make, always remember that you are going to be successful if you acquire the most appropriate equipment. If you are searching around for induction melter for sale, aluminum melting furnace for sale, steel melting furnace for sale, iron melting furnace for sale, metal melting machine for sale, or induction melting furnace for sale, you may as well find the good melting furnace you have been looking for!
Aluminum melting furnace
Aluminum, as a metal, has various industrial and commercial usages, such as in packaging (can, foil, etc.), transportation, building and construction, electricity and electrical devices, and, of course, used as household appliances (utensils and furniture).
Due to its popular application as a non-ferrous metal, it becomes essential for aluminum to be obtained in a form that it can retain its good properties.
Mostly, aluminum occurs in its alloy form. Though, it could be found in its compound forms (as Aluminum oxides, chlorides, phosphates, etc.), aluminum has also been discovered as a naturally occurring element in space and on earth.
The alloys of aluminum have diverse properties and applications as highlighted in the table below:
| Characteristic | Commercially pure aluminum | Heat-treatable alloys | Non-heat treatable alloys |
| Series | 1xxx Series (1350; 1100) | 2xxx Series (2024); 6xxx series (6061); 7xxx series (7050; 7075) | 3xxx series (3003); 4xxx series (4043); 5xxx series (4043) |
| Applications | Used for transmission or power grid lines | Used for Architectural and structural projects | Used in building and construction works |
| Types of strengthening | Naturally strengthened | Heat-treated | Cold-treated/Cold-working |
| Purity | Highest purity (about 99 percent) | Lower purity | Lowest purity |
To obtain aluminum in its purest form, it is imperative to melt aluminum from its alloys or compounds. Before now, several procedures have been applied to extract pure aluminum from its alloys or oxides. Some of these processes or methods include:
- Bayer process: This process is used to convert bauxite into aluminum oxide. After grinding and blending bauxite, it is added to a solution of sodium hydroxide (that is hot), and the mixture is treated in digester vessel which has a temperature that is above the atmospheric temperature. After cooling the resulting solution, the bauxite residue is separated from the remaining aluminum oxide and discarded. The aluminum oxide can be obtained in small crystals.
- Hall-Heroult process: This process converts alumina into a metallic aluminum. A solution of cryolite with calcium fluoride are then electrolyzed to obtain the metallic aluminum. It is reported that this method (Hall-Heroult Method) is able to produce an aluminum with the highest purity that is above 99 percent.
But the two procedures described above have not been commercially viable—this means that when thinking of producing aluminum in large, industrial quantity, Bayer and Hall-Heroult process are not recommendable. Hence, for modern production of aluminum, the use of induction aluminum melting furnaces has become the main practice in the industry.
5.1, Types of aluminum melting furnaces
The most common examples of aluminum melting furnaces are outlined below. You will read about their working principles and features:
5.1.1 Gas fired aluminum melting furnace
Check out 3.1.2 of this guide to read the principle of gas fired furnace.? You need a gas to power this kind of furnace to produce the required heating that will be used to melt metals. However, if you choose common gases such as hydrogen, helium, methane or ammonia, you may get less energy when compared with butane and propane that often produce high amount of energy.
Some gas fired aluminum melting furnaces have great features such as:
- 100% cold charging with an external charge well
- It requires manageable amount of gas per pound of metal to be melted
- If you preheat, 50% of the metals will charge as ingots
- It has high-velocity burners
- Melting in batch is possible
- It leaves the environment clean and with reduced or less pollution
A gas fired furnace by Schaefer Furnaces
5.1.2 induction furnace
Aluminum induction melting furnace comes in different types: We have manual, hydraulic, tilting, chain, or integrated. This section looks at how to use chain tilting electric induction furnace to melt aluminum.
The following features of chain tilting induction furnace makes it commercially useful for melting aluminum:
- Like every other type of induction furnace, the IGBT technology consumes very low amount of power. It, as a matter of fact, saves between 15 and 30% of energy, 100% when compared with a full-loaded KPGS.
- It produces low pollution and noise.
- It can work 24 hours nonstop.
- It doesn’t need a large area of space for its installation—it covers just less than 1 square meter.
- The replacement for the crucible is very easy and can be done as quickly as possible (within 1 minute).
- This kind of furnace comes with multi-purpose protection against over-voltage, over-current, over-heating, and less water.
- The installation and maintenance of chain tilting induction furnace are easy.
The picture below reveals a tilting induction furnace that can be used to melt aluminum. The tilting controller, a joystick, is used to tilt the crucible in order to pour out the molten aluminum during the melting procedure. It is possible to set or adjust the tilting speed.
5.1.3 Biomass pellet smelting furnace
If you are mostly concerned about the environment when melting aluminum, you may consider using a biomass pellet smelting furnace. The principle of this kind of furnace is simple: Instead of using an electric power, oil, or gas as the fuel, you will use biomass renewable energy. This is a low-cost energy and it makes the environment clean and safe.
Biomass pellet smelting furnace has various applications, in die-casting machine, incinerator, boiler, drying equipment or plant, smelting furnace, and so on. Its high-thermal property makes it energy efficient, and it is easy to operate.
5.1.4 Resistance Furnace
When using an electric resistance aluminum melting furnace, your attention should be placed on the technology behind its operation. Here are some facts for your consideration’
- The crucible is separate from the furnace and the aluminum to be melted is placed in the crucible.
- The crucible can be made of silicon carbide.
- It guarantees increased production and efficiency.
- It allows increased heating temperature through the hike of the power intake, from 100kW to 500kW.
- The rate of the resistance crucible is proportional to the surface area of the crucible.
- It guarantees constant crucible conductivity over a long period of time.
- It encourages high melt rate.
5.2, The processes of melting aluminum
The process for melting aluminum using an induction furnace is similar to those of other metals, such as copper described in section 3.2. However, there are other essential details of induction furnaces that must be explained:
- For a chain tilting induction melting furnace, you will use a joystick as the tilting controller. In this case, if you want to tilt the molten aluminum out of the crucible, all you need to do is to move the joystick sideway.
- Every induction metal melting furnace has the following features which make it possible for them to perform a good melting process:The Furnace Mouth: This comprises of the main part of the machine where the aluminum (or metal) to be melted will be deposited. The most important device in the furnace mouth is the crucible. The great thing about the crucible produced on an induction furnace is that it could be replaced in 1 minute.Control Panel: On the control panel, you can set the necessary parameters for melting your aluminum. These parameters include but are not limited to timing, speed, temperature, and other buttons for essential aluminum melting operations. The control panel is fully digitalized and, in some machines, it could be done remotely.Motor: This device is responsible for moving the parts of the furnace that are required for the machine to perform its functions very well.NOTE: It must be stated even though each type of induction metal melting furnace has similar parts and features, they also sometimes have slight differences in the way they are operated. Take for instance, manual tilting induction furnace can be tilted with hand, while hydraulic induction melting furnace is tilted with the help of a hydraulic mechanism.
5.3, Conditions necessary for good aluminum melting
To have a good aluminum melting outcome, it is imperative that serious attention must be given to the following issues:
- Melt loss reduction: It is the best practice out there to reduce the amount of melt loss during aluminum melting. The good news is that induction metal melting furnaces are designed to successfully handle this issue—by reducing the quantity of melt loss, unlike the one common to foundries.
- Dross generation: During the process of melting aluminum, dross is generally produced. Using the good technology in IGBT induction technology, this produce of dross production will be drastically reduced.
- Heat nature: It is also important to pay attention to the different types of aluminum alloys that we have. The 1xxx Series are considered to be naturally pure and do not necessarily require melting. While 2xxx, 6 xxx, and 7 xxx series are heat-treatable, the 3xxx, 4xxx, and 5xxx are not heat-treatable. What this signifies is that the temperature required for melting each alloy, oxide, or compound of aluminum must be properly controlled in order to achieve better result or outcome.
- Slag reduction: Efforts must also be placed into reducing the amount of slag produced while melting aluminum. However, it is necessary to state that the induction metal melting furnaces are built to eliminate or reduce the production of slag.
Precious Metal Melting Equipment
Precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, and so on need to be melted and refined before you can use them for whatever purpose you want. Precious metals are used as ornaments or in the making of jewelry. Some of them are good conductor of electricity, hence they are used in electrical devices and cables.
Silver, for example, is used in producing currencies. You will need some specialized equipment to carry out your precious metal melting. This section highlights some useful equipment that you can use.
6.1, Equipment for melting precious metals
There is a list of precious metal melting equipment that you can utilize, from induction melting furnace to propane burner and arc furnace. 6.1.1 Induction melting furnace Nowadays, some of the furnaces used for melting precious metals adopt the induction technology. The technology increases the overall efficiency of the melting process. If you are using this kind of equipment, it is possible for you to achieve a very fast melting time, usually within 2 minutes per each batch. Induction furnaces are environmentally good, save energy, and come with all the necessary protection. Your induction furnace will have a great power design which makes it to function non-stop for 24 hours. In fact, its maximum temperature can be as high as 1600℃. This makes it suitable for melting precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, aluminum, and their corresponding alloys. The quantity each furnace can handle depends on its design and capability. An induction gold melting furnace can melt as little as 1g, up to 2kg.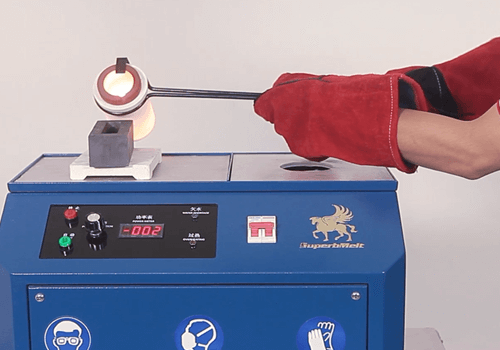 6.1.2 Propane burner
A typical propane burner is filled up with propane (gas), which is used to melt gold and other precious metals. This can produce enough heat needed to melt precious metals. If you want to make a small bar of gold, you can decide to make your propane burner at home.
All you need to do is to buy the parts of a burner and carefully assemble it. Make sure you systematically follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer. You should also understand that when using the burner in oxygen environment produces more heat than using the same in ordinary air.
6.1.2 Propane burner
A typical propane burner is filled up with propane (gas), which is used to melt gold and other precious metals. This can produce enough heat needed to melt precious metals. If you want to make a small bar of gold, you can decide to make your propane burner at home.
All you need to do is to buy the parts of a burner and carefully assemble it. Make sure you systematically follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer. You should also understand that when using the burner in oxygen environment produces more heat than using the same in ordinary air. 6.1.3 Arc furnace
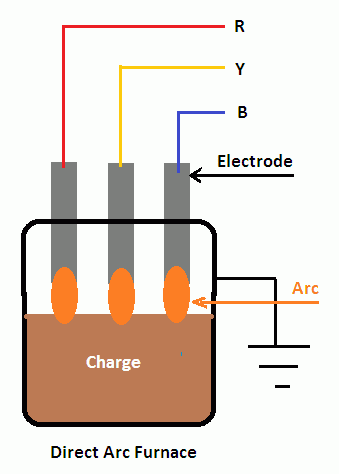
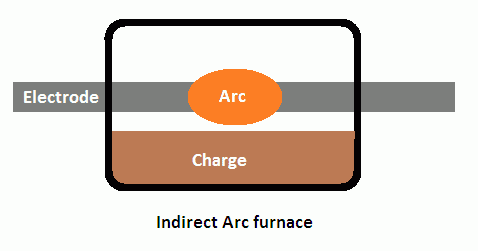
An electrical furnace is also a good equipment for melting gold and other precious metals. There are two different types of arc furnaces: Direct arc furnace, and indirect arc furnace.
In direct arc furnace, its chamber is lined with materials that are refractive in nature. The arc is positioned between the electrode and charge. There are three electrodes that are made of graphite or carbon. These electrodes are projected from the top of the furnace. A three-phase supply is provided, and the current goes through them via the charge (material to be melted). This reveals that the arc is in direct contact with the charge; this makes it possible for this kind of furnace to produce the highest temperature for melting.
On the other hand, an indirect arc furnace is formed between the two electrodes and the heat that is produced gets to the charge through radiation. Because there is no direct contact with the charge, the heat produced by indirect electrical charge is lower when compared with the heat generated by direct electrical arc furnace.
6.1, Equipment for melting precious metals
The three types of furnaces outlined above are useful for different purposes. If you are targeting a very small-scale precious metal melting (mostly at home or in a small foundry), it is advisable that you should use the propane burner. It is the cheapest and less dangerous.
However, for a medium-sized foundry or metalworking workshop, the electric arc furnace may be used. Its production capacity is larger than that of the propane burner, but it is less than that of the induction melting furnace.
The induction melting furnace for the precious metals are the latest technology in town. Its capability is huge, and the amount of materials it can handle increases based on the design of the furnace. It is also the safest and more efficient method for melting precious metals.
6.3, Equipment for melting precious metals
Unlike other kinds of metals, the precious metals are more delicate and destructible. So, it is important that they are handled with utmost care. To obtain a good result while melting precious metals, the following safety measures are necessary:
- Corrosive nature: Precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, and others can corrode if they are not handled carefully. It means they can lose their shining surface when scratched. So, make sure your precious metals are not stored or placed near other metals or hard materials that can scratch them.
- Oxidation: When exposed to excess oxygen during melting, most precious metals can be oxidized. When oxidation takes place, a precious metal may lose its physical or even chemical properties. To obtain precious metals in their natural and good states, it is advisable that an anti-oxidation environment should be used. All induction melting furnaces have anti-oxidation systems. Otherwise, the precious metals can be covered with inert gases to prevent oxidation during the melting processes.
- Impurities: Sometimes, some alloys of certain precious metals may contaminate the final precious metal if the melting procedure is not done well. In this case, it is important to note the different melting points of the constituent elements in order to guarantee that they are perfectly melted and the precious metals are purified.
How to choose the best metal melting furnace
You need to concentrate on choosing the most useful metal melting furnace for your operations if you want to get great results.
7.1, 10 important factors to consider while choosing the best metal melting furnace
- Size: Depending on the size of your operations, selecting a furnace that will deliver exactly what you need should be your priority. There is small, medium, and large metal melting processes. If your melting capacity is below 1kg, you may go for a small furnace. But if you are aiming for more than 25kg capacity, it is advisable you should get a large furnace or a tilting mechanism that will allow fast pouring-out and re-filling of crucibles with the molten metals.
- Efficiency: Induction metal melting furnace is considered a very effective melting equipment because of its good technology that makes melting easy as ABC. Since its invention, induction melting furnace has helped metalmaking companies improve not only their performances but also profitability.
- Safety: In everything, even in metal melting business, safety comes first. Look for melting furnaces that will provide the required protection for your workers as well as your business.
- Durability: Choose a metal melting equipment that can last for many years. Getting a durable furnace will help you save on yearly overhead or cost of running your business.
- Easy installation: You should go for a melting furnace that is very easy to install or maintain. You will save money you should have spent on periodical maintenance if your melting furnace is difficult to manage by you or your staff.
- Technology: Most of the metal melting furnaces in town utilize technologies that are peculiar to their making or designs. Choose the one that is the most suitable or useful for your metal melting goals.
- Cost: If you are starting out as a metalmaking company owner, you may want to consider the cost or price of getting a melting furnace before settling down on one.
- Compatibility: Sometimes you may need to combine one or two technologies together to achieve better metal melting performance. In that case, choose a melting furnace that can work well with other technologies.
- Environmentally friendly: Nowadays, every country makes laws that will make sure your melting operations will not affect the environment or the people living in it. So, buy a furnace that is less polluting and has no harmful effects on people working in your company. More information about environmental friendliness is provided below.
- Warranty: Do not buy a melting furnace that has no warranty on it. This means that the manufacturer is not quite sure of the quality of their products. You should ask for, at least, one or two years warranty on whatever furnace you are buying.
7.2, Environmental and legal considerations while using a metal melting furnace
The reason why some countries make it necessary for operators of metalmaking companies to obtain licenses before operating is to make sure that their operations are legal and environmentally friendly.
Here are some important legal and environmental considerations you should take before or in the course of operating a metal melting company:
- Location: Make sure you choose a place that is not in the middle of a residential area to avoid being disrupted by the other residents may claim that your plant or factory is making too much noise.
- Government papers and licenses: Obtain all the required documents before starting your metalmaking factory or company. Some delegations from local health or business affairs ministries may visit your factory to be sure it is designed or built to the standards.
- Less pollution: Only use equipment or machines that will produce minimal or no noise, water, air, and land pollution. It is mostly unacceptable in many nations to run a metal melting operation that is dangerous to human health and safety. So, make sure you are using a technology that can guarantee some safety for people.
- Renewable technology: One of the best ways to reduce or eradicate pollution is to use the latest technology in metal melting. Take for instance, the induction melting furnaces are known for their clean and pollution-free operations. It is very important that you use a melting furnace that has renewable wastes. With this, you do not need to worry about disposing off the wastes coming from the furnace.
- Permissions or permits: Depending on your location, you may need to get some permissions or permits before you can operate a metal melting furnace or factory. If you have done the right thing at first, you will be able to operate your factory with peace of mind without necessarily worrying about being sued by people or prosecuted by the local authorities.
Summary
This final chapter takes a critical look at the other factors that you must consider before setting up an effective metal melting operation. You must be legal and responsible; this means that you will be operating within the confines of laws and regulations in your locality. To achieve this, you may be required to obtain some permits, permissions, or licenses. You will buy melting furnaces that will produce little or no pollution and has a renewable technology. You will equip your metalmaking factory with protective gadgets or devices so that your workers can operate without any fear.
Conclusion
This comprehensive metal melting guide has taken you through all the most important steps you need to know as far as metal melting process is concerned. You have also learned about the different types of melting furnaces and how to use them.
As additional information, you need to understand that each country or locality has distinct laws and regulations that guide their metal melting operations. So, do the necessary research to find out which legal and environmental considerations you must have before starting your metal melting business or factory.
You should also pay attention to the manufacturers’ instructions and guidelines if you want to obtain the most desirable results from your metal melting processes. Do not forget that each manufacturer has separate specifications as far as their equipment is concerned; so, stick to their instructions if you want your melting furnaces to have longer shelf-life.
Remember to create a good working environment for your workers and furnaces. Operating in a dusty and dirty environment can damage the equipment within a short period of time. And exposing your workers to a dangerous working condition or environment can destroy their health and reduce their performance or productivity.
It is advisable that you acquire the right kinds of metal melting furnaces that will handle your scale of metalmaking operations. You may purchase an equipment for melting metal with electricity. However, if you are operating small-scale, then a machine for melting bronze at home or mini metal melting furnace may be appropriate. The main considerations here are cost, efficiency, and longevity of those machines. If you bought a furnace that cannot last for a long time you may be required to buy another one very soon. This is applicable to used or second-hand metal melting furnaces. New furnaces can last for a long time, and this is why it is often reasonable to purchase new equipment directly from the manufacturers. But if you are facing financial constraints and wish to manage the little funds you have, you can try your hand on a used furnace but make sure it will work well for a long time.
If you do not know how to go about getting a good metal melting furnace, why don’t you contact a manufacturer’s sales team? They will advise you about the right thing to do.





















 © Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited