Induction Crucible Melting Furnace
The Most Popular SuperbMelt 1-2kg mini gold (Ag, Cu, Al etc) melting furnace on the market

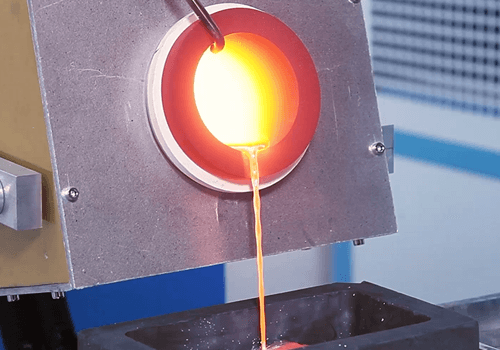
SuperbMelt induction crucible melting furnace is designed to melt different precious metal elements using various types of crucibles. It can melt various metals such as gold, silver, copper, etc., ranging from 10 to 250 kilograms at a time.
The Induction Crucible Melting Furnace features a hydraulic tilting design, allowing for remote pouring operations, making it convenient and safe to use.
The SuperbMelt Induction Crucible Melting Furnace is the perfect choice for large jewelry casting facilities, addressing rapid production needs efficiently.
Power Supply Parameter of Induction Crucible Melting Furnace
| Model | HMF-15 | HMF-25 | HMF-35 | HMF-45 | HMF-70 | HMF-90 | HMF-110 | HMF-160 | |
| MAX input power | 15KW | 25KW | 35KW | 45KW | 70KW | 90KW | 110KW | 160KW | |
| MAX input current | 23A | 36A | 51A | 68A | 105A | 135A | 168A | 240A | |
| Input voltage | Three-phase 340V ~420V 50/60Hz | ||||||||
| Oscillation frequency | 1K~20KHz | ||||||||
| Requirement of cooling water | Hydraulic pressure | ≥0.2Mpa | ≥0.3Mpa | ||||||
| Flow rate | ≥6L/Min | ≥20L/Min | |||||||
| Temperature of water | ≤45℃ | ||||||||
Melting Capacity Parameter of Tilting Metal Melting Furnace
| Model | Fe, ss | Cu, Au, Ag | Al, Al-alloy | Model | Fe, ss | Cu, Au, Ag | Al, Al-alloy | |
| HMF-15 | 3kg | 10kg | 3kg | HMF-70 | 25kg | 80kg | 25kg | |
| HMF-25 | 5kg | 20kg | 5kg | HMF-90 | 40kg | 120kg | 40kg | |
| HMF-35 | 10kg | 30kg | 10kg | HMF-110 | 50kg | 150kg | 50kg | |
| HMF-45 | 18kg | 50kg | 18kg | HMF-160 | 100kg | 250kg | 100kg | |
| Remark: Above melting capacity sheet for general reference; Melting duration: When the crucible is hot,20~30min./workload; When the crucible is cold(first melt),40~50min./ workload. | ||||||||
Features:
- Efficient Melting: SuperbMelt’s induction crucible melting furnace is renowned for its efficient melting of various metals, including precious metals like gold and silver. They can rapidly achieve high melting temperatures.
- Precise Temperature Control: Crucible furnaces feature a precise temperature control system, enabling you to accurately maintain the desired melting temperature.
- Safety: Induction crucible furnaces are designed with remote electric hydraulic tilting for pouring, preventing accidents, and incorporating protective measures to reduce exposure to high temperatures.
- Versatility: Induction crucible melting furnaces can melt a variety of metals, making them suitable for various applications in industries such as jewelry manufacturing, casting, and metal recycling.
- Clean and Environmentally Friendly: Induction heating is a clean and environmentally friendly process as it does not involve open flames or emissions of harmful gases.
Advantages:
- High Energy Efficiency: Crucible furnaces have high energy efficiency as they can convert a high proportion of electrical energy into heat, reducing energy consumption and costs.
- Rapid Melting: They possess rapid heating capabilities, reducing processing time and increasing productivity.
- Uniform Heating: Induction heating provides uniform and consistent heating throughout the entire metal, ensuring even melting and improved product quality.
- Reduced Metal Loss: Precise control and uniform heating reduce metal loss due to overheating or incomplete melting.
- Remote Operation: Induction crucible melting furnaces are equipped with features such as hydraulic tilting, enabling remote and safe pouring and operation.
- Low Maintenance Costs: These furnaces generally have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance compared to other melting methods.
- Controlled Atmosphere Options: Some models offer controlled atmosphere options to protect sensitive metals from oxidation during the melting process.
Why SuperbMelt Induction Crucible Melting Furnace



Any Question About SuperbMelt Induction Crucible Melting Furnace
SuperbMelt Induction Crucible Melting Furnace Guide
Application Field Of Gold Melting Equipment
Most people may see Arthur Miller’s well-known play when they hear the word “crucible,” or they may picture a trying time in a person’s life that puts their fortitude to the test. A crucible, however, has a quite different meaning in the fields of science and industry. This container, built to resist and hold extreme heat, serves as the basis for many transformative processes. Let’s set out on a voyage to comprehend the crucible world, its many varieties, and its importance in a number of fields.
- Describe the Crucible
A crucible’s basic function is to act as a container for materials that can be heated to extremely high temperatures. But this straightforward explanation obscures the significance of the crucible. This device has aided developments in metallurgy, chemistry, and material science for millennia, enabling us to create the materials and compounds that are the foundation of contemporary civilisation.
- The Importance of Crucibles in History
Examples of how crucibles have shaped civilisation can be found throughout human history. When early civilizations engaged in metallurgical activities, they understood the importance of a container that could endure high temperatures. These early crucibles were essential to the scientific accomplishments of ancient nations, helping them forge copper tools and create jewellery.
The sophistication and power of crucibles increased over time. Alchemists were employing them by the time the Middle Ages came around in their attempts to transform base metals into gold. They never succeeded in achieving that elusive goal, but their efforts lay the foundation for contemporary chemistry.
1.1, Smelting The Gold Ores
The term “crucible” often evokes images of alchemists laboring over bubbling concoctions, or perhaps the metaphorical trials faced by individuals in challenging circumstances. However, in a more literal and technical sense, a crucible is a container used for heating substances to high temperatures, and they come in a variety of types and materials to suit specific applications. These containers are crucial in scientific research, metallurgy, and industrial processes. Let’s explore the different types of crucibles and what sets them apart.
- Clay-Graphite Crucibles
Clay-graphite crucibles are perhaps the most commonly used type and for good reason. They are manufactured by blending clay and graphite, and this composition enables them to withstand extremely high temperatures. Used extensively in metal foundries, they’re ideal for melting metals such as aluminum and copper. One of their main advantages is affordability. However, they can be susceptible to cracking or thermal shock if not handled properly, and they may interact with specific materials, which could be a limitation in some experiments.
- Silicon Carbide Crucibles
Silicon carbide (SiC) crucibles are a step up in terms of both cost and durability. They are less susceptible to cracking and can handle temperature changes more efficiently compared to clay-graphite crucibles. Because of their robustness, they are often used in industrial processes that require prolonged exposure to high temperatures and aggressive chemical environments. However, their high cost can be a deterrent for smaller labs or operations.
- Quartz Crucibles
Quartz crucibles are transparent and offer excellent thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for tasks that require constant monitoring. They are mostly used in labs for chemical analysis and quality control due to their ability to withstand corrosive materials. However, quartz crucibles have a limited temperature tolerance compared to clay-graphite or silicon carbide variants.
1.2, For Recycling Old Gold
Melting precious metals is a nuanced task that requires specialized equipment and techniques. Among the most important tools for this process is the crucible, a container designed to hold materials at high temperatures. The type of crucible you choose can dramatically impact the purity, quality, and even safety of your operation. Whether you’re dealing with gold, silver, platinum, or other precious metals, let’s delve into which types of crucibles are best suited for melting these valuable elements.
- Clay-Graphite Crucibles: The Affordable Option
For many, the first stop on the quest for the perfect crucible is the clay-graphite variety. Composed of a mixture of clay and graphite, these crucibles are particularly effective at withstanding high temperatures. They are also relatively affordable, making them an accessible option for small-scale operations or for those just entering the realm of metal melting. While the graphite helps improve thermal conductivity, the clay content gives the crucible structural integrity.
However, it’s essential to note that clay-graphite crucibles are somewhat porous, meaning they can absorb some of the metal or any additives used in the process. Over time, this can lead to contamination issues, especially if you’re switching between different types of metals in the same crucible. Also, these crucibles can deteriorate faster than other types, requiring frequent replacements.
- Silicon Carbide Crucibles: Durable but Costly
Silicon carbide crucibles come with a higher price tag but offer excellent durability and efficiency. They are non-porous and therefore less susceptible to absorbing materials. If you’re working with high-value metals like gold and platinum and wish to avoid any form of contamination, silicon carbide crucibles offer a more reliable choice. They also have a higher resistance to thermal shock, meaning they are less likely to crack when exposed to rapid temperature changes.
- Platinum Crucibles: The Premium Choice
Most often, graphite or high-quality ceramic crucibles are used to melt platinum. For smaller-scale platinum melting procedures, ceramic crucibles are frequently utilised, whereas graphite crucibles are better suited for larger-scale processes. The quantity of platinum being melted and the exact requirements of the melting process determine which option is best.
1.3, For Jewellery Casting
Consider the kind of substance you’ll be melting or processing when choosing a material. Different substances call for different crucible substances. For instance, although ceramic or quartz crucibles may be preferable for materials that react with graphite, such as some ceramics or glasses, graphite crucibles are excellent for metals such as gold, silver, and copper.
Make sure the crucible material can sustain the temperature needed for your process by checking its resistance to temperature. Materials like alumina or zirconia may be required for high-temperature applications.
Chemical Resistance: Choose a crucible material that is chemically inert and won’t react with the components being processed if your procedure calls for corrosive or reactive ingredients.
Decide on a crucible’s size and shape based on the application for which it will be used. Think about the amount of stuff you’ll be handling and the area your furnace or other heating device has to offer.
Determine the crucible’s anticipated life span in this section. Consider the long-term expense of replacements because some materials may wear out more quickly than others.
Application Type: Depending on your procedure, you could require a particular crucible design, such as a tundish for pouring or a cover for shielding the substance during heating.
1.4, For Industrial Applications
Crucibles act as containers to store and keep the substance contained while it is being melted or treated inside the induction furnace. This containment is necessary to prevent the molten material from spilling or dispersing, which could endanger safety and cause equipment damage.
Thermal insulation: High-temperature resistant materials, including graphite, ceramics, or refractory metals, are frequently used in the construction of crucibles. Thermal insulation offered by these materials helps to sustain the high temperatures needed for melting while shielding the furnace’s induction coils and other components from direct exposure to extremely hot temperatures.
Crucibles act as containers to store and keep the substance contained while it is being melted or treated inside the induction furnace. This containment is necessary to prevent the molten material from spilling or dispersing, which could endanger safety and cause equipment damage.
Thermal insulation: High-temperature resistant materials, including graphite, ceramics, or refractory metals, are frequently used in the construction of crucibles. Thermal insulation offered by these materials helps to sustain the high temperatures needed for melting while shielding the furnace’s induction coils and other components from direct exposure to extremely hot temperatures.
Chemical compatibility: The exact material being processed will determine the type of crucible material to use. Induction coils or the lining of a furnace can sustain damage from some compounds, particularly reactive or corrosive ones. Crucibles serve as a barrier, making sure that the molten material only comes into contact with the material of the crucible and not the other parts of the furnace.
Facilitating Pouring: Spouts or handles are frequently incorporated into crucible designs to make it simpler to pour or transfer molten material into moulds or other receptacles. This makes manipulating the melted material more accurate and controlled.
Protection of Induction Coils: If the molten material came into touch with the induction coils directly during induction melting, the extreme heat may cause damage. Crucibles serve as a barrier that shields against harm and lengthens the life of the coils.
Contamination Control: Maintaining material purity is essential in some applications. By isolating the molten substance from its surroundings, crucibles can aid in the prevention of contamination.
Uniform Heating: Crucibles aid in ensuring that the material is heated uniformly. The crucible material facilitates consistent and effective melting by distributing electromagnetic energy from the induction coils uniformly throughout the substance.
Induction Furnace
An electrical furnace known as a “induction furnace” is used to melt metals, heat materials, and carry out other heat-treatment procedures. By passing alternating current (AC) through a coil of wire and creating a magnetic field, it works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a metal object is placed in this magnetic field, the electric currents that are induced cause the metal to heat up quickly.
Induction furnaces are frequently used in a variety of industrial applications, including:
Metal Melting: They are widely used for melting and casting a variety of metals, including precious metals like gold and silver as well as steel, iron, copper, and aluminium.
Heat Treatment: To attain particular material qualities, metals and alloys are heated through procedures like tempering, annealing, and hardening in induction furnaces.
Foundries: For the metal casting and moulding processes, foundries use induction furnaces.
Forging: Metal components are forged and shaped using induction heating.
Brazing, soldering, and other welding techniques can all use induction heating for localised heating.
Surface Hardening: Surfaces of components are hardened to increase wear resistance.
Numerous benefits come with induction furnaces, such as quick heating, accurate temperature control, excellent energy economy, and a hygienic working environment. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from compact benchtop units used in labs to enormous industrial-scale furnaces for demanding applications.
The extensive use of induction furnace technology makes it a flexible and effective solution for a variety of materials and processes. These sectors require precise and controlled heating or melting.
2.1, How To Melt Gold By The Use of Propane Kiln
An induction furnace is a device that uses electromagnetic induction to provide a controlled environment for melting and heating a variety of materials, principally metals and alloys. The following are an induction furnace’s main duties:
- Melting Metals: An induction furnace’s main use is to efficiently and swiftly melt metals and alloys. This is accomplished by creating an alternating magnetic field inside of a coil, which causes electrical currents (called eddy currents) to be induced in the metal that is placed within the furnace. Due to resistance, these currents produce heat, which causes the material to melt quickly.
- Induction furnaces provide operators with fine temperature control, enabling them to maintain certain melting temperatures as needed for various materials and applications. In order to create high-quality metal castings or get the correct material characteristics during heat treatment, this accuracy is necessary.
- Heating Consistency: The material being treated is heated uniformly and consistently throughout thanks to induction heating. In order to achieve homogeneous melting and preserve material integrity, it is essential that the entire material achieves the necessary temperature equally.
- Induction furnaces are well renowned for being energy efficient. Compared to conventional heating technologies, they minimise energy waste and save running expenses by converting a high percentage of electrical energy into heat.
- Clean and Controlled Environment: Since induction heating doesn’t use open flames or fuel burning, it has a low impact on the environment and emits less dangerous gases. The regulated climate also aids in keeping the melted substance uncontaminated.
- Versatility: Induction furnaces have a wide range of uses, including melting metal, heat treating (such as annealing, tempering, and hardening), foundry operations, forging, welding, and more. They are appropriate for a variety of sectors because to their versatility.
- Safety: To ensure the protection of operators and avoid accidents, these furnaces are built with safety measures. The use of remote controls, barrier protection, and temperature monitoring systems are all examples of safety precautions.
- Fast Heating: When compared to conventional heating techniques, induction furnaces can reach high temperatures quickly, reducing processing times and increasing output.
In conclusion, the main purpose of an induction furnace is to uniformly, precisely, and efficiently melt and heat materials, especially metals and alloys. It is a flexible and essential instrument in the industrial and metallurgy sectors and is widely used in a variety of industries for procedures that call for regulated and quick heating.
2.2, What is a Crucible Induction Furnace?
An induction furnace specifically made for melting and heating metals, alloys, and other materials in a crucible is known as a “Crucible Induction Furnace”. It offers a controlled and effective melting process by combining the ideas of electromagnetic induction with crucible technology.
A Crucible Induction Furnace has an induction coil, much like conventional induction furnaces do. When an alternating current (AC) flows through this coil, it creates an alternate magnetic field. Eddy currents are electric currents that the magnetic field causes to form inside the conducting crucible.
- Crucible: A crucible is a container used to melt materials. It is often constructed of ceramic or graphite and is composed of conductive material. The induction coil is filled with the crucible. The magnetic field causes eddy currents to form in the crucible, which heats up the material inside the crucible and eventually causes it to melt.
- System of Control: Crucible Induction The precise temperature control systems and power supply units that are included into furnaces enable operators to set and maintain the required melting temperature. This guarantees that the melting process will be accurate and consistent.
- Safety Features: To prevent mishaps and guarantee safe operation, these furnaces are built with safety features including over-temperature prevention and emergency shut-off systems.
- Important Induction In situations where controlled melting of metals and alloys is necessary, furnaces are frequently utilised. Examples of typical uses include:
- Aluminium, bronze, and cast iron are just a few of the metals and alloys that are cast at foundries using crucible induction furnaces.
- Jewelry-making: Crucible induction furnaces are used to melt precious metals like gold and silver to make jewellery.
- Laboratory and Small-Scale Applications: These furnaces are employed for research, development, and specialised melting procedures in labs and small-scale production facilities.
Crucible induction furnaces are frequently used for metal component prototyping and small-scale manufacturing.
Crucible induction furnaces have the benefit of being versatile and effective in melting tiny to moderate amounts of materials with accuracy and control. In fields and applications that need precise and regulated melting operations, they are an invaluable tool.
Conclusion
SuperbMelt Crucible Induction Furnace represents the epitome of precision and efficiency in the world of metal melting and heating. Just as a crucible has been a fundamental tool throughout history, the Crucible Induction Furnace by SuperbMelt continues to play a pivotal role in various industries and applications.
The versatility of this induction furnace is second to none, accommodating a wide range of materials, from precious metals like gold and silver to industrial metals such as aluminum and copper. Its ability to achieve rapid and precise temperature control ensures that the melting process is not only efficient but also consistent, meeting the stringent requirements of modern metallurgy and material science.
Safety is paramount, and the Crucible Induction Furnace is designed with robust safety features, including over-temperature protection and emergency shut-off mechanisms, guaranteeing a secure working environment for operators.
Whether you are a jewelry manufacturer seeking to create exquisite pieces, a foundry in need of reliable metal casting, or a laboratory conducting cutting-edge research, the SuperbMelt Crucible Induction Furnace is your trusted partner. Its durability and efficiency make it an ideal choice for both small-scale operations and large-scale industrial applications.
With options like clay-graphite crucibles for affordability, silicon carbide crucibles for durability, and even platinum crucibles for the most demanding processes, SuperbMelt offers a range of crucible choices to meet your specific needs.
In a world where precision, efficiency, and safety are paramount, the SuperbMelt Crucible Induction Furnace stands as a testament to innovation and excellence, empowering industries to achieve their melting and heating goals with unparalleled reliability. Experience the future of metal melting and heating with SuperbMelt today.
About the Induction Crucible Melting Furnace FAQ
- 1. What is the crucible in an induction furnace?
- 2. What is difference between crucible and furnace?
- 3. What is the function of crucible furnace?
- 4. What types of crucibles are suitable for use in this furnace?
- 5. In which industries is the Induction Crucible Melting Furnace commonly used?
- 6. Can Induction Crucible Melting Furnaces be used for both small-scale and industrial applications?
- 7. How does the choice of crucible affect the quality of the melted material?
- 8. What are the safety features of Induction Crucible Melting Furnaces?
1. What is the crucible in an induction furnace?
In an induction furnace, the crucible is a container or vessel used to hold and contain the material that is being melted or heated by the electromagnetic induction process. The crucible is typically made of a conductive material, such as clay-graphite, silicon carbide, or quartz, depending on the specific application and material being processed.
2. What is difference between crucible and furnace?
A crucible and a furnace are two distinct components used in metallurgy and various industrial processes, often in conjunction with each other. Here are the key differences between the two:
Function:
Crucible: A crucible is a container designed to hold and contain materials, typically solid substances, that need to be heated to extremely high temperatures. It acts as a vessel for melting or heating materials and is usually made of materials that can withstand high temperatures, such as clay-graphite, silicon carbide, or quartz. Crucibles are passive components used to contain and protect the material during heating.
Furnace: A furnace is a device or apparatus used for the controlled heating of materials. It is an active component that generates and maintains the required high temperatures for various processes, including melting, forging, heat treatment, and more. Furnaces are responsible for providing the heat needed to achieve specific material transformations.
Components:
Crucible: The crucible itself is a single-piece container. It is typically made of a heat-resistant material, and its design may include features such as spouts or handles for pouring molten material.
Furnace: A furnace is a more complex system consisting of multiple components, including heating elements (e.g., induction coils or resistive heating elements), insulation, temperature control systems, and sometimes a crucible placed within it. The furnace generates and controls heat to achieve specific temperature profiles.
Role:
Crucible: The primary role of a crucible is to contain and protect the material being heated or melted. It prevents spillage, contamination, and loss of material during the heating process.
Furnace: The primary role of a furnace is to provide the necessary heat to raise the temperature of the material within the crucible to the desired level. Furnaces come in various types, including induction furnaces, electric arc furnaces, and others, each designed for specific applications.
Operation:
Crucible: A crucible is a passive component that relies on external heat sources, such as a furnace, to heat the material inside it. It does not generate heat on its own.
Furnace: A furnace is an active heat-generating device. It uses heating elements or other heat sources to produce the required temperatures for various processes. The crucible may be placed within the furnace to hold and protect the material.
3. What is the function of crucible furnace?
- A crucible furnace is a type of furnace that uses a crucible as its heating chamber or vessel. The function of a crucible furnace is primarily to provide a controlled and localized heating environment for various industrial processes.
- Melting: Crucible furnaces are commonly used for melting materials, especially metals and alloys. They can rapidly heat the contents of the crucible to their melting points, allowing for the transformation of solid materials into molten form. This is essential in metal casting, foundries, jewelry making, and other industries where melting is a crucial step.
- Heat Treatment: Crucible furnaces are also used for heat treatment processes, such as annealing, tempering, and hardening of metals and alloys. These processes involve controlled heating and cooling cycles to achieve specific material properties and hardness levels.
- Chemical Reactions: In some applications, crucible furnaces are used to carry out chemical reactions that require high temperatures. They can provide a controlled environment for reactions involving substances that need to be heated to extreme temperatures.
- Research and Development: Crucible furnaces are used in research laboratories and development facilities for experimentation and testing. They offer a controlled and repeatable heating environment, making them valuable tools for materials science and process development.
- Small-Scale Production: These furnaces are suitable for small-scale production and prototyping. Industries that produce custom or limited quantities of specialized components often use crucible furnaces.
- Precise Temperature Control: Crucible furnaces are equipped with temperature control systems that allow operators to maintain specific temperature profiles, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
- Safety: The use of crucibles within a furnace provides a safe containment vessel for materials during heating. This prevents spillage, contamination, and the escape of potentially hazardous substances.
- Uniform Heating: Crucible furnaces are designed to distribute heat evenly within the crucible, ensuring uniform heating of the material. This uniformity is crucial for achieving consistent results in metallurgical and material processing.
- Versatility: Crucible furnaces can be used for a wide range of materials, including various metals, ceramics, and other heat-treatable substances.
4. What types of crucibles are suitable for use in this furnace?
Suitable crucibles include clay-graphite crucibles, silicon carbide crucibles, and quartz crucibles, depending on the material being melted and specific application requirements.
5. In which industries is the Induction Crucible Melting Furnace commonly used?
It is widely used in industries such as metal casting, jewelry manufacturing, laboratory research, small-scale production, and various metalworking applications.
6. Can Induction Crucible Melting Furnaces be used for both small-scale and industrial applications?
Yes, these furnaces are suitable for both small-scale laboratory applications and large-scale industrial processes due to their versatility and precision.
7. How does the choice of crucible affect the quality of the melted material?
The choice of crucible material can impact material purity, quality, and the potential for contamination. Proper selection ensures the desired results in the melting process.
Feel free to ask if you have more specific questions or require further information about Induction Crucible Melting Furnaces.
8. What are the safety features of Induction Crucible Melting Furnaces?
Safety features may include temperature protection, emergency shut-off mechanisms, remote operation, and temperature monitoring systems to protect operators and prevent accidents.


 © Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited