Silver Refining Electrolysis
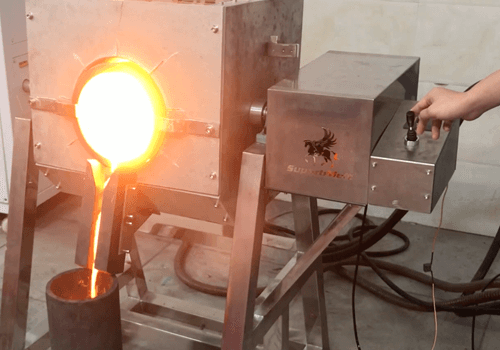
SuperbMelt automated silver refining machine is widely used in the industrial production and recycling of silver. It effectively removes impurities and produces high-purity silver.


SuperbMelt Silver Refining Electrolysis machine can refine and purify up to 100kg of silver in a single operation, achieving a purity level of typically over 99.99% by removing impurities.
Compared to traditional refining methods, the automated Silver Refining Electrolysis machine from SuperbMelt can accelerate the refining process, improve production efficiency, and consistently maintain purity levels above 99.99%, resulting in the production of high-purity silver and enhancing the quality and performance of the final products.
Silver Refining Electrolysis plays a crucial role in industries such as jewelry, medical, and electronics, enabling the production of superior quality products through the refinement of silver. If you are interested in learning more about our electrolytic purification solutions, please don’t hesitate to contact us for further information.
| Model number | SPB-DJM100 |
| Power source | 3 phase 380V, 50/60Hz |
| Power | 15 kw |
| Applicable metal | Gold, Silver, copper |
| Capacity | 300-500kg |
| Production volume: | 24h*100kg silver |
| Dimension | 4500x1100x1024mm |
| Water cooling requirement | ≥0.3Mpa, flow rate≥20L/min, ≤45℃ |
| Dimension | 4500x1100x1024mm |
- Efficient Electrolysis Process: Utilizes the principle of electrolysis to dissolve the anode (925 silver) in the electrolyte, depositing it onto the cathode to form metallic silver. This process ensures efficient refining of silver.
- Flexible Anode Options: Offers flexibility in anode selection with options for titanium blue plates or hanging silver plates, allowing customization based on refining requirements.
- Durable Cathode Design: Features titanium cathode plates with a scraper, ensuring durability and effective collection of silver slag.
- Robust Electrolytic Cell: Constructed with porcelain white imported PP plates, welded channel steel reinforcement, and anti-corrosion properties, providing a robust and durable electrolytic cell.
- Optimized Conductivity: Utilizes titanium-clad copper strips for the cathode and anode, ensuring excellent conductivity and reliable performance throughout the electrolysis process.
- Convenient Operation and Maintenance: Equipped with a conveyor belt for easy collection of silver slag and a circulation tank for electrolyte replacement, facilitating convenient operation and maintenance.
- Compact Design: Features compact outer dimensions (4500x1100x1024mm), optimizing space utilization in industrial settings.
- High-Frequency Pulse Rectifier: Equipped with a high-frequency pulse power supply (15V, 1000A) and a 15kW rectifier, ensuring stable and efficient power delivery for the electrolysis process.
- Included Stainless Steel Shipping Bucket: Comes with a 316 stainless steel shipping bucket, providing a convenient solution for transporting refined silver.
- Jewelry Manufacturing: Used for purifying silver to create high-quality jewelry and ornaments.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Employed in producing high-purity silver materials required for medical equipment and instruments.
- Electronics Industry: Provides high-quality silver for manufacturing electronic components, circuit boards, and conductive materials.
- Photography and Printing: Utilized in the production of silver salts for photographic films, printing materials, and photosensitive materials.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries: Produces high-purity silver for catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and chemical synthesis applications.
- Currency and Investment Sector: Supplies high-purity silver for the production of minted silver coins, bars, and other investment products.
- Crafts and Decorative Arts Manufacturing: Used in creating high-quality crafts and decorative items.

Continuous 24-hour operation to refine 100kg of silver to 99.99% purity.

The electrolyte circulation device keeps the electrolyte in the refining machine in a continuous flow, ensuring stable silver purification quality.

Store the refined silver products in a dedicated storage box.
Why SuperbMelt Silver Refining Electrolysis



More SuperbMelt Silver Refining Electrolysis and Casting Equipment For Your Choice
Any Question About SuperbMelt Silver Refining Electrolysis
SuperbMelt Silver Refining Electrolysis Guide
Silver mining
The process of mining silver is intricate and involves many steps and factors. The first step is geological exploration, which uses drilling, sampling, and geological surveys to assess the quality and reserves of the silver ore. An environmental impact assessment is then conducted to determine the possible consequences of mining operations on the surrounding area and to secure the required environmental approvals and permits. The design and planning of the mine is then started in order to decide on the layout and mining techniques and to create comprehensive mining plans. Construction of the necessary infrastructure, such as roads, transit hubs, electricity supplies, and water sources, follows. In order to guarantee safe production, personnel recruitment and training are carried out concurrently with the purchase and installation of mining equipment and supporting facilities. Continuous monitoring and control of mining progress, environmental effects, and safety concerns are required throughout the mining process. As needed, mining plans must be optimized and adjusted. In conclusion, the process of tailings treatment and mine site restoration is executed, which encompasses the appropriate management of mining residues as well as the ecological reconstruction and restoration of the mining region. By taking these precautions, silver mining can be carried out effectively and securely, maximizing resource usage and safeguarding the environment.
1.1, Surveying
- Geological Survey: Conduct geological surveys to understand the area’s geological structure, lithology, and mineral deposit formation. This may include creating geological maps and collecting and analyzing geological samples.
- Geophysical Survey: Use geophysical methods such as seismic surveys, gravity surveys, and electromagnetic surveys to detect the structure and characteristics of underground deposits.
- Geochemical Survey: Employ geochemical methods to analyze soil, water, and rock samples for characteristic elements or chemical anomalies around the deposit.
- Exploratory Drilling: Use exploratory drilling equipment to collect core samples from potential mining areas, providing further insight into the underground rock structure and mineralization.
- Surveying and Marking: Conduct land surveying and marking to determine the boundaries and features of the survey area, providing accurate geographical references for subsequent work.
- Data Analysis and Evaluation: Analyze and evaluate the collected geological, geophysical, and geochemical data to identify the potential location and value of the mineral deposit.
1.2, Crushing
Using crushers to process mined silver ore involves primary and secondary crushing stages to reduce large ore chunks into smaller particles. This process includes screening and grading to ensure the particle sizes meet the requirements for subsequent processing and extraction. This improves the efficiency and effectiveness of ore handling, preparing it for further milling and silver extraction.
1.3, Smelting
Weighing and Getting Ready:
Weigh and get ready for the smelting process of the silver material, such as silver ore.
Make sure the material is clean and dry to prevent interference with the smelting process.
Filling up:
Put the silver material inside the induction melting furnace’s crucible.
For better smelting efficiency and to assist eliminate impurities, add the right amount of flux (such as borax).
Melting:
Turn on the furnace for induction melting. The material may be quickly heated and melted using electromagnetic induction.
To guarantee that the silver is completely melted and achieves the required purity, regulate the heating time and temperature.
Eliminating Spills:
Use flux and other chemicals in the crucible during the melting process to purge the silver of impurities.
In order to guarantee the quality of the melted silver, regularly skim out slag.
Casting:
Pouring: To create silver ingots, bars, or other desired shapes, pour the pure molten silver into molds that have been previously prepared.
Before taking the completed item out of the molds, let the silver cool and harden.
Cleaning and Cooling:
Cooling: To hasten the cooling process, utilize cooling equipment or allow the silver ingots to cool naturally.
After the silver ingots have cooled, clean the surface to get rid of any remaining contaminants and flux.
Benefits
Effective Heating:
Introduction Melting furnaces use electromagnetic induction to quickly heat materials, enabling quick and effective smelting.
Accurate Management:
There is less chance of overheating or underheating when the temperature is accurately regulated to guarantee even melting of the silver.
Elevated Pureness:
High-purity silver is produced by efficiently removing contaminants through the use of flux and refining processes.
Safety in the Environment:
Induction melting furnaces have a reasonably eco-friendly heating technique that minimizes dangerous gas emissions and maintains a high level of operating safety.
Adaptability:
suitable for smelting a variety of silver materials in varying compositions and shapes to meet a range of industrial requirements.
How is silver refined?
Several techniques are used in the refining of silver, depending on the scale of the operation and the needed purity. The parting process, chemical refining, pyrometallurgical refining, and electrolytic refining are the most widely used techniques. To manufacture high-purity silver that is appropriate for industrial, investment, and decorative uses, these processes entail steps including melting, dissolving, precipitating, and electrolyzing in order to remove impurities.
2.1, Why does silver need refining?
Silver refining is the process of removing impurities from silver-containing materials, such as silver ore, scrap silver products, and silver alloys, through a series of techniques and processes to obtain high-purity silver. The purpose of silver refining is to enhance the purity of silver to meet the demands of various industries including industrial, medical, jewelry, and investment sectors. This process is vital for ensuring the quality and performance of silver and has significant implications across industries. There are various methods of silver refining, including electrolytic refining, pyrometallurgical refining, chemical refining, and separation methods, each with its unique advantages and applications.
2.2, Why does silver need refining?
For a number of significant reasons, silver must be refined in order to attain high purity and eliminate impurities:
- Industrial Applications: Since even minute impurities can compromise conductivity and performance, high-purity silver is crucial for sectors like electronics. Impurities can lower efficiency in industries like solar energy, where photovoltaic cells use silver.
- Jewelry and Cutlery: The sheen and visual appeal of pure silver make it highly valued for use in jewelry and cutlery. Impurities that could impact appearance and workability are eliminated during refining.
- Investment and Monetary Use: To retain its worth and reputation as a store of wealth, silver used for investment reasons, such as bullion coins and bars, must adhere to strict purity requirements.
- Applications in Medicine and Health: High-purity silver is essential for ensuring biocompatibility and lowering the possibility of negative responses or contamination in medical equipment and devices.
- Scientific Research: Accurate findings in a large number of scientific experiments and investigations require high-purity silver. Impurities have the potential to disrupt experiments or jeopardize the accuracy of study results.
- Environmental Aspects: Recycling silver from scrap and abandoned goods not only helps avoid resource depletion but also helps reduce contamination of the environment. Refined silver is fit for reuse in a variety of applications by eliminating contaminants.
- In general, silver refining is necessary to guarantee the metal’s performance, quality, and compatibility for a range of commercial, industrial, and scientific uses.
2.3, Silver refining methods
Refining electrolytically:
Process: Silver is purified by electrolysis. An electrolyte solution, pure silver, and impure silver are utilized as the cathode and anode, respectively. Impurities are left behind as silver ions move from the anode to the cathode of the cell when an electric current is applied.
Advantages: Removes most contaminants effectively and can reach very high purity levels (up to 99.99%).
Refining pyrometallurgically:
Method: In a furnace, materials containing silver are melted, impurities are oxidized to generate slag, which is subsequently removed to reveal pure silver.
Benefits: Easy to use and appropriate for handling big amounts of material processing.
The Wohlwill Process of Chemical Refining:
Process: Dissolves contaminants from silver by chemical processes. After dissolving silver in a solution of nitric acid, more chemicals are added to precipitate out pure silver.
Benefits: High-purity silver is produced and tiny batches of silver may be refined effectively.
Process of Parting:
Method: consists of alloying silver with another metal (such as copper), precipitating pure silver from the alloy after it has been dissolved in a chemical solvent to remove impurities.
Benefits: Very helpful in distinguishing silver from other metals, such gold.
Each of these techniques has benefits of its own and is applied in accordance with the particular needs of the application, the amount of material being refined, and the required purity level.
Applications of silver refining equipment
3.1, Old silver recycling
Refiners of silver are essential for recovering old silver by extracting and purifying it into high-grade silver. These devices make it possible to efficiently process items used to make scrap silver, such as old jewelry, cutlery, electronic components, and industrial scrap, into pure silver that can be kept or sold again. Recycling facilities can reduce waste and save important resources by extracting valuable silver from old or abandoned goods using silver refining equipment. This procedure supports recycling operations’ financial sustainability in addition to environmental sustainability.
3.2, Currency and investment field
Refining machines for silver ensure the manufacturing of high-purity silver products, which is essential for the currency and investment industries. These devices play a key role in the currency industry when it comes to purifying silver to achieve the purity requirements needed to issue coins and create other monetary instruments. These devices guarantee the integrity and worth of silver money by purifying it to the appropriate purity levels, which increases investor and consumer confidence.
For the investment industry to produce premium silver coins, bars, and bullion, refiners are a must. Investment-grade silver goods are guaranteed to be of the highest quality and authenticity thanks to these machines, which refine silver to the purity standards desired by investors. These devices generate high-purity silver, which supports the precious metals market’s liquidity and confidence by adding to the asset’s stability and appeal as an investment.
All things considered, silver refining machines are essential to the currency and investment industries because they make it easier to produce high-purity silver goods that satisfy the exacting standards of quality demanded in these fields.
3.3, Jewelry manufacturing industry
Without silver refining equipment, the jewelry manufacturing industry cannot operate for a variety of reasons.
Obtaining High-Purity Silver: Jewelry manufacturers require high-purity silver to ensure the worth and caliber of their goods. Contaminants can be eliminated from raw materials to create high-purity silver that can be utilized to make excellent jewelry by using technology that refines silver.
Preserving Consistency in Quality: The manufacture of jewelry need a steady grade of silver. Refinement devices contribute to the maintenance of consistent purity levels, which in turn results in uniformity in the appearance, attributes, and functionality of silver jewelry.
Enhancing Workability: Due to its increased ductility and malleability, high-purity silver is simpler for jewelers to work with. By removing impurities that could affect the metal’s workability with refining machines, artisans can create intricate designs and achieve the desired finishes.
Increasing Aesthetic Appeal: The attractive appearance and stunning brilliance of pure silver make it the ideal material for jewelry. The improved sheen, brilliance, and color of silver produced by refining equipment increases the jewelry’s aesthetic appeal.
Respecting Regulatory rules: Jewelry producers are required to abide by regulatory rules regarding the purity of silver used in their goods. Refining machinery yields silver at predefined purity levels, enabling adherence to these requirements.
Sustainability and Efficiency: Reusing old silver jewelry and scrap metal is a regular practice in the industry to reduce waste and mitigate its adverse impact on the environment. Silver refining machines facilitate recycling and promote sustainability and resource conservation by extracting pure silver from waste sources.
In summary, the jewelry business greatly depends on silver refining machines to provide high-purity silver that meets quality standards, enhances workability, preserves consistency, and improves the appearance of silver jewelry products.
Advantages and disadvantages of refining silver by electrolysis
4.1, Advantages
Benefits of electrolytic silver refining:
High Purity: The creation of very pure silver is ensured by the very high degrees of purity that electrolytic refining can produce, frequently surpassing 99.9%.
Impurity Removal That Is Selective: Electrolysis makes it possible to remove impurities one at a time, leaving silver with little to no contamination.
Efficiency: The method works well for industrial-scale refining operations since it can be scaled up to handle enormous volumes of silver.
Process Controlled: Electrolysis provides exact control over electrolyte composition, voltage, and current, among other refining factors, enabling quality control and repeatable outcomes.
Environmentally Friendly: Electrolysis is a more sustainable solution because it generates less waste and has a less environmental impact than other refining techniques.
4.2, Disadvantages
Negative aspects of using electrolysis to refine silver
Energy-Intensive: The process of electrolytic refining necessitates a large energy input, mostly in the form of electricity, which may raise operational expenses.
Complexity: The electrolytic refining process can be complicated and calls for specialized tools and knowledge, which raises the cost of the original investment and complicates operations.
Slow Processing Time: The refining process may take longer to finish using electrolysis than it would with some other processes, particularly for big amounts of silver.
Chemical Hazards: If the electrolyte solutions used in the process are not handled correctly, they may include toxic compounds that could endanger the health and safety of the personnel.
Initial Investment: Smaller-scale operations may not be able to afford the substantial capital expenditure in equipment and infrastructure needed to set up an electrolytic refining plant.
How to cast platinum group metal
Given its vital role in so many sectors and the new trends reshaping the global economy, silver’s future seems bright. Due to its special qualities, including as its high conductivity and reflectivity, silver is still used in a wide range of electrical, renewable energy, and medical technologies. In the next years, the demand for silver is anticipated to increase due to the shift towards sustainable energy sources like solar power and the increasing number of electric cars. Furthermore, investors looking to protect themselves against inflationary pressures and economic instability find silver to be appealing due to its role as a store of value and investment asset. Notwithstanding, the silver market is confronted with obstacles including limited supply and fluctuations in the market, which may have an effect on future price movements. Notwithstanding these obstacles, possibilities exist to fulfill rising demand in a sustainable manner because to continuous technical advances and improvements in mining and recycling techniques. Overall, despite current concerns, silver’s future is bright because of its inherent qualities and crucial role in promoting economic development and technological progress.
Conclusion
The conversation around silver refining machines highlights how important they are to a number of sectors and businesses, from the production of jewelry to the fields of investments and renewable energy. In order to extract, purify, and process silver to the high purity standards required by contemporary manufacturing methods and customer expectations, these devices are essential instruments.
By using techniques such as chemical reactions, pyrometallurgical refining, and electrolysis, silver refining machines may convert raw silver resources into high-purity silver that can be used in a wide range of applications. They are essential resources in manufacturing processes, research facilities, and recycling facilities because of their capacity to eliminate impurities, regulate refining parameters, and guarantee consistency in the quality of silver.
With further technological developments, rising consumer demand for premium silver goods, and a growing focus on resource efficiency and sustainability, the future of silver refining machinery seems bright. The production of exquisite jewelry, electronic components, and renewable energy technologies are just a few of the many uses for which silver refining machines will be essential as industries continue to develop and change.
But issues like energy use, operational complexity, and environmental concerns highlight the need of ongoing research and development to improve the sustainability and efficiency of silver refining procedures. The silver refining sector may further streamline production processes, lessen its effect on the environment, and meet the changing needs of a dynamic global market by tackling these issues and using innovative technology.
In summary, silver refining machines are not only incredible pieces of technology, but also vital catalysts for advancement and creativity in a variety of sectors. These devices are essential to the future development of sustainable development, economic progress, and technology because they can convert raw silver resources into refined, high-purity silver.
1. how to refine silver with electrolysis?
- Gather the silver-containing materials (silver ore, scrap silver, or silver alloys) that need to be processed. In order to maximize the refining process, make sure the material is dry and free of impurities.
- Establish Electrolytic Cell: Get ready to set up an electrolytic cell with an impure silver anode and pure silver cathode submerged in an electrolyte solution. Silver nitrate solution or other appropriate electrolytes are often used as the electrolyte.
- Apply a direct electric current to the electrolytic cell to start the electrolysis process. While contaminants stay behind and settle as sludge or are deposited on the anode, the electric current drives silver ions from the anode to travel towards the cathode.
- Control Parameters: To maximize the refining process and guarantee effective impurity removal, monitor and regulate critical parameters including voltage, current, temperature, and electrolyte composition.
- Gather Pure Silver: A layer of refined silver is formed on the cathode as a result of pure silver being deposited there while electrolysis proceeds. To get rid of any leftover electrolyte or contaminants, periodically remove the silver that has been deposited from the cathode and clean it.
- Get Rid of Impurities: Get rid of any impurities that were gathered at the anode, such as residues or sludge that included base metals and other pollutants.
- Repeat if Necessary: The electrolysis process may need to be repeated many times in order to reach the required degree of purity, depending on the starting purity of the silver material and the refining objectives.
- Final Purification: Additional purification techniques like zone refining or chemical refining may be used to further purify the silver if ultra-high purity is needed.
- Quality Control: To confirm the purity of the refined silver and make sure it satisfies the necessary requirements, conduct quality control tests using techniques such assaying or spectroscopic analysis.
- Storage and utilize: After being refined, keep the pure silver in the proper containers or utilize it straight away for a variety of purposes, such investment items, jewelry creation, and electronics manufacture.
2. What is the electrolyte for silver refining?
Typically, a solution including silver ions (Ag⁺) and other supporting ions to aid in the electrolysis process makes up the electrolyte utilized in silver refining. AgNO₃ (silver nitrate) solution is the most often used electrolyte in the silver refining process because it provides silver ions.
Because silver nitrate dissolves readily in water, creating electrolyte solutions with different concentrations is a simple process. Silver nitrate is also ideal for industrial refining procedures since it is stable and generally safe to handle.
Depending on the particular needs for refining or the parameters of the process, other electrolytes could be utilized in certain situations. For instance, solutions of silver cyanide (AgCN) or silver sulfate (Ag₂SO₄) may be used in certain electroplating or refining processes.
3. Can silver be refined by electrolysis?
Yes, electrolysis may be used to purify silver. One popular and efficient technique for removing impurities from sources of pure silver, such as ore, scrap silver, or silver alloys, is electrolytic refining. An electrolytic cell is built up in this procedure, with a cathode (pure silver) submerged in an electrolyte solution and an anode (impure silver). Silver ions move from the anode to the cathode when an electric current flows through the cell, where they deposit as pure silver.
By precisely controlling the refining process, electrolytic refining makes it possible to remove contaminants from the silver material, including copper, lead, and other base metals. Regulation of variables including voltage, current, temperature, and electrolyte composition may alter the refined silver’s purity. All things considered, electrolytic refining is a popular and efficient process for creating high-purity silver appropriate for a range of commercial, industrial, and investment uses.
4. What is the process of refining silver?
To extract and purify silver from raw materials, which might include ore, scrap silver, or silver alloys, the refining process entails a number of procedures. Silver may be refined using a variety of techniques, including chemical refining, ash blowing, and electrolysis, although electrolysis is most often used because of how well it can produce high purity. This is a summary of the electrolysis method used to refine silver:
- Material preparation: Gather the material to be refined that contains silver and make sure it is clean, dry, and devoid of impurities. Silver alloys, scrap silver, and silver ore might all be included in this item.
- Set up the electrolytic cell: Assemble an electrolytic cell by submerging the cathode (pure silver) in an electrolyte solution and the anode (impure silver). To aid in the refining process, the electrolyte usually includes silver ions and other supporting ions.
- Applying a direct current to the electrolytic cell will initiate electrolysis. Silver ions move from the anode to the cathode when current flows through the cell. Sludge-like precipitates or deposits of impurities in the silver substance may still be seen on the anode.
- Control parameters: To maximize the refining process and guarantee efficient impurity removal, monitor and regulate critical parameters including voltage, current, temperature, and electrolyte composition.
- Gathering Pure Silver: A layer of refined silver is formed on the cathode as a result of pure silver being deposited there during the electrolysis process. Periodically, the deposited silver is taken out of the cathode and cleaned to get rid of any contaminants or leftover electrolyte.
- Handling Impurities: Sludge or residue containing base metals and other pollutants are examples of impurities that are collected at the anode and dealt with.
- Repeat as necessary: To reach the required purity level, the electrolysis process may need to be performed many times, depending on the starting purity of the silver material and the refining objectives.
- Final Purification: Additional purification processes like chemical or regional refining may be used to further purify the silver if ultra-high purity is needed.
- Quality Control: To confirm the purity of the refined silver and make sure it satisfies the necessary requirements, quality control procedures like assays or spectroscopic analysis are carried out.
- Storage and Use: Following refinement, pure silver is either immediately employed in a variety of purposes, such as investment goods, jewelry production, or electronics manufacturing, or it is kept in suitable containers.
5. How is scrap silver refined?
- Preparing the Scrap: Collect the silver scrap that has to be refined, such as silverware, jewelry, or other objects that contain silver. Make sure the scrap is uncontaminated and clear of non-metallic materials.
- Melting: In order to create a homogeneous liquid mass, any solid scrap silver must first be melted down. This may be accomplished using a furnace or other melting apparatus that can melt silver at 961.8°C, or 1763.2°F.
- Sampling and Assaying: Use assaying to ascertain the composition of the melted silver by taking a representative sample. In order to guide the refining process, this entails examining the sample to determine the proportion of silver and any impurities present.
- To refine silver electrolytically, set up an electrolytic cell with pure silver as the cathode and impure silver as the anode submerged in an electrolyte solution. Silver ions go from the anode to the cathode of the cell when a direct electric current is applied. The leftover impurities in the scrap silver material might either settle as sludge or end up on the anode.
- Control Parameters: To maximize the refining process and guarantee effective impurity removal, monitor and regulate critical parameters including voltage, current, temperature, and electrolyte composition.
- Gather Pure Silver: A layer of refined silver is formed on the cathode as a result of pure silver being deposited there while electrolysis proceeds. To get rid of any leftover electrolyte or contaminants, periodically remove the silver that has been deposited from the cathode and clean it.
- Get Rid of Impurities: Get rid of any impurities that were gathered at the anode, such as residues or sludge that included base metals and other pollutants.
- Repeat if Necessary: The electrolysis process may need to be repeated many times in order to reach the required degree of purity, depending on the starting purity of the scrap silver and the refining objectives.
- Final Purification and Quality Control: Additional purification processes like zone refining or chemical refining may be used if ultra-high purity is needed. Conduct quality control procedures, such as spectroscopic analysis or assaying, to confirm the refined silver’s purity and make sure it satisfies the necessary requirements.
- Storage and utilize: After being refined, keep the pure silver in the proper containers or utilize it straight away for a variety of purposes, such investment items, jewelry creation, and electronics manufacture.
- These procedures may be used to efficiently refine scrap silver into pure, high-grade silver that can be used for a variety of commercial, industrial, and investment applications.














 © Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited